10 Resource Allocation Strategies to Optimize Projects in Excel

Resource allocation is the critical process of assigning your most valuable assets—people, time, and budget. When done effectively in a tool like Excel, you accelerate growth and hit targets with precision. When done poorly, you face project delays, team burnout, and wasted capital. The fundamental challenge lies in shifting from reactive guesswork to a structured, data-driven system within your spreadsheets.
This article cuts through the complexity by breaking down 10 proven resource allocation strategies. We provide a clear roadmap for implementing each one directly within Excel, transforming your spreadsheets from simple trackers into powerful planning tools. You will learn not only the "what" and "why" behind methods like Agile and Zero-Based allocation but also the practical "how-to" for your worksheets.
Furthermore, we'll demonstrate how integrating AI tools, such as Microsoft Copilot or dedicated Excel add-ins like Elyx.AI, can automate analysis and surface insights you might otherwise miss. This allows you to move beyond manual data entry and focus on making informed, strategic decisions. Get ready to turn your planning challenges into competitive advantages, ensuring every resource is deployed for maximum impact.
Spending too much time on Excel?
Elyx AI generates your formulas and automates your tasks in seconds.
Try for free →1. Priority-Based Resource Allocation
Priority-Based Resource Allocation is a straightforward yet powerful strategy where you distribute resources according to a ranked list of tasks or projects. This method ensures that your most critical initiatives receive the funding, time, and talent they need to succeed before any resources are assigned to lower-value activities. It's about making conscious decisions to support what matters most, directly within your planning tools.
This approach forces organizations to define what "important" truly means. For instance, Apple consistently allocates a significant portion of its R&D budget and top engineering talent to its flagship iPhone development. This laser focus prevents resources from being diluted across less strategic projects.
How to Implement in Excel
To effectively use this strategy in Excel, you must first establish a clear system for ranking priorities. A formal scoring model that balances urgency with long-term strategic value is crucial.
- Create a Scoring Matrix: In a new Excel sheet, create columns for "Project Name," "Strategic Alignment (1-5)," "Potential ROI (1-5)," "Urgency (1-5)," and "Total Score." Use a simple formula like
=SUM(B2:D2)to calculate the total score for each project. - Use Conditional Formatting: Apply color scales or data bars to the "Total Score" column to visually distinguish high-priority projects from low-priority ones. This provides an instant visual reference for stakeholders.
- Automate with AI: Ask an AI tool like Elyx.AI or Copilot to "Analyze the project list and identify the top 5 projects based on the scoring criteria." This saves time and removes manual sorting errors.
The following infographic summarizes the core principles of this resource allocation strategy for quick reference.
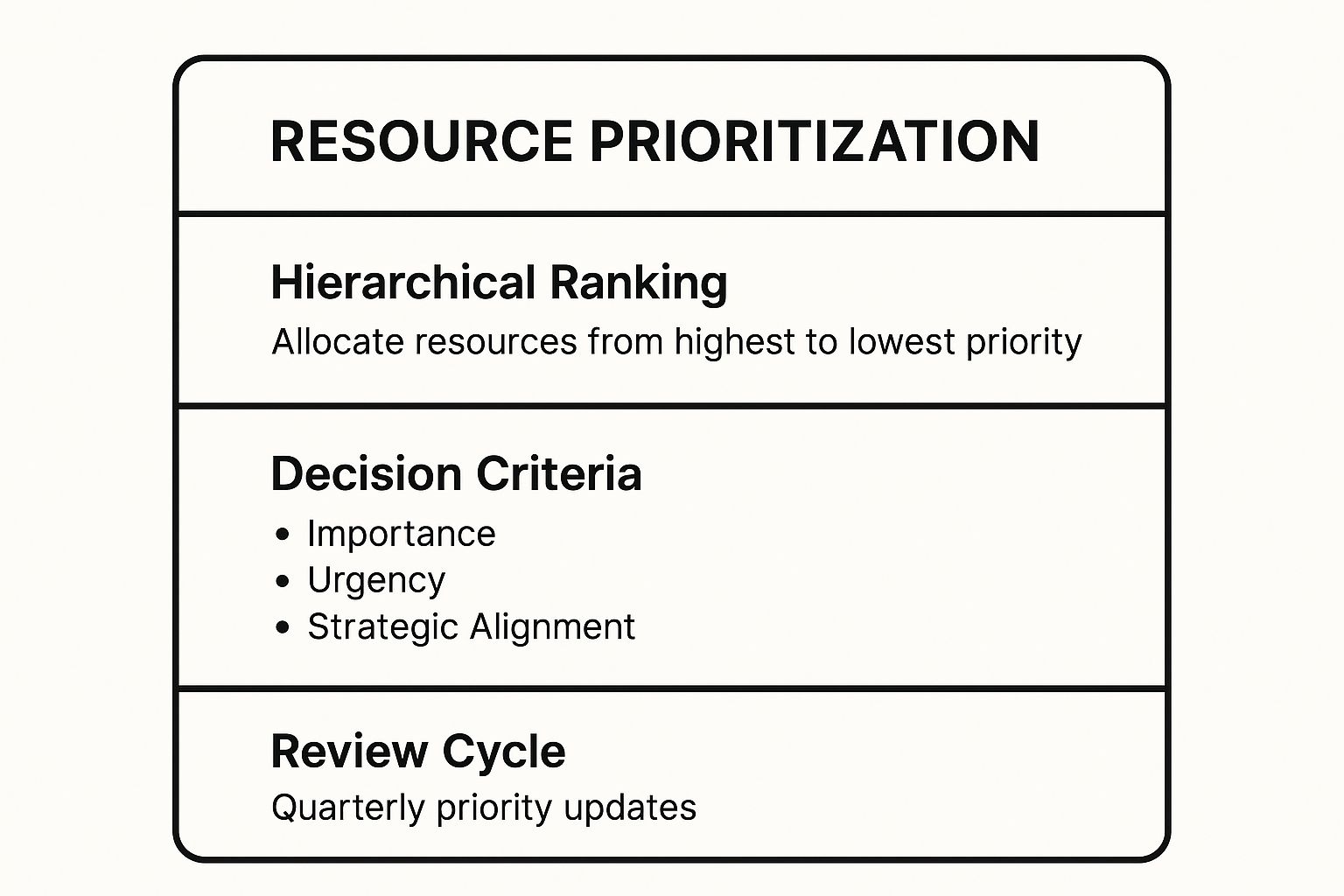
This visual highlights the structured process: rank initiatives, apply clear decision criteria, and maintain agility through regular reviews. By documenting the rationale behind these decisions in your spreadsheet, you create transparency and ensure everyone understands why certain projects get the green light.
2. Agile Resource Allocation
Agile Resource Allocation is a dynamic strategy that distributes resources in short, iterative cycles, emphasizing flexibility and continuous adaptation. Instead of locking in budgets and teams for long periods, this approach allocates talent and funding for brief sprints, allowing for regular reassessment based on performance and feedback. It moves resource management from a static annual plan to a responsive, ongoing process.
This method, born from software development, is designed for unpredictable environments. For example, Spotify’s famous squad-based model empowers autonomous teams to pull the resources they need for specific feature development sprints, enabling fast innovation.

How to Implement in Excel
Implementing agile resource allocation strategies requires a cultural shift towards empowerment and dynamic planning. For a comprehensive understanding of the framework, delve into Mastering the Agile Project Management Methodology.
- Build a Sprint Backlog: Create a simple Excel table with columns for "Task," "Sprint," "Assigned To," "Status," and "Estimated Hours." Use data validation to create dropdown lists for status (e.g., To Do, In Progress, Done).
- Visualize with a Kanban Board: Use Excel shapes or a pre-made template to create a simple Kanban board directly in a worksheet. Link the shapes to your backlog data so they update automatically as the status changes.
- Leverage AI for Analysis: After each sprint, use an AI tool to analyze the data. A prompt like "Summarize the completion rate and total hours worked for Sprint 3 from the backlog sheet" can instantly generate a performance report, helping you re-allocate resources for the next sprint.
This fluid approach ensures that resources are consistently directed toward the most valuable initiatives at any given moment, preventing waste and maximizing organizational agility.
3. Zero-Based Resource Allocation
Zero-Based Resource Allocation (ZBRA) is a rigorous strategy where every resource request starts from a "zero base" in each new planning cycle. Instead of adjusting the previous period's budget, this method requires all departments to justify their needs from scratch. It challenges the status quo and forces a deep evaluation of every expense.
This approach eliminates budget inertia. For example, Unilever implemented a zero-based budgeting initiative that reportedly saved over $1 billion by forcing managers to scrutinize every cost and align spending directly with current strategic goals.
How to Implement in Excel
Effective implementation requires a shift in mindset from incremental budgeting to value-based justification. A structured Excel template is essential.
- Create Justification Templates: Build a standardized Excel template for managers. Include fields for "Activity," "Resource Requested (Cost/Hours)," "Justification," and "Link to Strategic Goal." This ensures consistency.
- Use Pivot Tables for Review: Consolidate all justification sheets into a master workbook. Use a PivotTable to summarize requests by department, strategic goal, or cost type. This allows for a high-level review of all requests.
- Automate with AI: To speed up the review, ask an AI assistant: "From the consolidated budget requests, identify all line items over $10,000 that are not linked to a Tier 1 strategic goal." This helps focus leadership attention on the most critical decisions.
4. Portfolio Management Resource allocation
Portfolio Management Resource Allocation is a holistic strategy that treats all organizational initiatives as a portfolio of investments. Resources are strategically distributed across a diverse mix of projects balanced by risk, return, and alignment with overarching business goals. This approach optimizes the entire portfolio's value rather than focusing on individual projects.
This method ensures a balanced investment. For instance, Procter & Gamble famously uses a 70-20-10 model, allocating 70% of resources to core innovations, 20% to adjacent markets, and 10% to transformational new ventures.
How to Implement in Excel
To effectively implement this strategy, you must categorize projects and establish clear portfolio balance targets within your spreadsheet.
- Categorize Projects: In your project list, add a "Category" column with options like "Core," "Adjacent," and "Transformational." Also, add a "Risk Level" (Low, Medium, High).
- Visualize with a Bubble Chart: Create a bubble chart in Excel. Set the X-axis as "Risk Level," the Y-axis as "Potential ROI," and the bubble size as "Budget Allocation." This creates a visual "Portfolio Map" that instantly shows where your resources are concentrated.
- Use AI for Optimization: Ask an AI tool to analyze your portfolio data: "Based on my 70-20-10 target, calculate the current allocation percentage for each project category and suggest adjustments to meet the goal."
By viewing resource allocation through this strategic lens, organizations ensure their investments are building a balanced future. For managing complex portfolios, learn more about project management tools in Excel to help visualize and manage performance.
5. Capacity-Based Resource Allocation
Capacity-Based Resource Allocation is a systematic approach that distributes work based on the actual availability and utilization rates of your team. This strategy ensures that resource demand does not exceed supply, preventing burnout and project delays. It's a pragmatic method focused on what your team can realistically accomplish.
This approach requires diligent tracking of who is available and their commitments. Consulting firms like McKinsey use sophisticated systems to allocate consultants to projects without exceeding their workable hours.

How to Implement in Excel
Effective implementation hinges on gaining real-time visibility into your resource pool and upcoming demand. Understanding top capacity planning strategies is a critical first step.
- Create a Capacity Tracker: Build a worksheet with team members listed in rows and weeks or months in columns. In each cell, enter their available hours (e.g., 40 hours/week).
- Track Allocation: On a separate sheet, list all projects and assigned team members with their allocated hours per week. Use a
SUMIForSUMIFSformula on the capacity sheet to subtract allocated hours from available hours. - Automate with AI: Use an AI add-in to simplify analysis. Ask: "Generate a chart showing the capacity vs. allocation for each team member for the next month and flag anyone over 85% utilization."
This visual represents the core of capacity management: balancing demand against your team's actual available hours. By maintaining this equilibrium, you create a more stable and predictable project environment.
6. Strategic Resource Allocation (Top-Down)
Strategic Resource Allocation is a top-down approach where senior leadership makes resource distribution decisions based on the organization's overarching strategic objectives. Resources flow from these high-level decisions downward, ensuring every allocation directly supports the company's long-term vision.
This strategy ensures capital is deployed with purpose. For example, Tesla's aggressive resource allocation to its Gigafactory expansion was a direct top-down decision by leadership to secure its future in battery production.
How to Implement in Excel
To effectively use this strategy, leadership must clearly define priorities that can be translated into an Excel model.
- Create a Strategic Goals Sheet: Dedicate one worksheet to listing the company's top 3-5 strategic goals for the year.
- Link Allocations to Goals: In your budget or resource plan, add a column "Strategic Goal Link." Use data validation to create a dropdown list that pulls directly from your goals sheet. This forces every resource request to be tied to a strategic priority.
- Use AI for Reporting: Ask an AI assistant to create a summary report: "Generate a PivotTable that shows the total budget allocated to each strategic goal." This provides leadership with a clear, data-driven view of how resources are supporting the company's vision.
By aligning resource allocation with high-level goals, companies can significantly boost their operational efficiency. Learn more about measuring these improvements to see the full impact.
7. Dynamic Resource Allocation (Market-Based)
Dynamic Resource Allocation treats your organization like an internal marketplace, where resources are distributed based on supply and demand. In this model, business units must "bid" for resources like talent or budget by demonstrating their potential value. This decentralized approach uses market principles to ensure resources flow to the most promising opportunities.
This strategy encourages an entrepreneurial mindset. For instance, W.L. Gore & Associates uses a commitment-based system where associates choose which projects to join, effectively "voting" with their time. This is one of the more advanced resource allocation strategies for fostering agility.
How to Implement in Excel
Creating an internal market in Excel requires clear rules and transparency.
- Establish a Bidding System: Create a shared Excel workbook where project leaders can post their resource needs (e.g., "Need a data analyst for 20 hours/week for Project X").
- Create Resource Profiles: Maintain a sheet with all available team members, their skills, and their current allocation. Use this as the "supply" side of the marketplace.
- Automate Matching with AI: Use an AI tool to act as the market maker. A prompt like, "Based on the project requests and available resource profiles, suggest three optimal matches for the data analyst role on Project X," can streamline the process and remove bias.
While complex, this model can drive significant innovation by ensuring resources are naturally drawn to high-impact initiatives.
8. Constraint-Based Resource Allocation (Theory of Constraints)
Constraint-Based Resource Allocation is a focused strategy where you identify the single biggest bottleneck limiting your system’s performance and direct resources to maximize its output. Instead of spreading efforts thinly, you concentrate on the one area that will have the greatest impact on overall throughput.
This approach, from Eliyahu Goldratt's "The Goal," argues that any complex system is governed by a few constraints. For example, if a software team’s bottleneck is QA testing, this strategy dictates allocating resources to streamline testing (e.g., automation tools) to increase the entire team’s output.
How to Implement in Excel
To leverage this strategy, you must use Excel to systematically identify, exploit, and elevate your primary constraint.
- Map Your Process: Use a simple flowchart or table in Excel to map the key steps in a process (e.g., Design > Develop > Test > Deploy).
- Track Throughput Data: For each step, collect data on processing time and wait time. The step with the longest queue or cycle time is your constraint. Use conditional formatting to highlight this bottleneck in your data table.
- Model Scenarios with AI: Once the constraint is identified, ask an AI assistant to model solutions. For example: "If I increase QA capacity by 20% in my process data, what is the projected impact on the total project lead time?" This helps justify resource allocation decisions.
This is one of the most effective resource allocation strategies for achieving significant performance gains with targeted investments.
9. Scenario-Based Resource Allocation
Scenario-Based Resource Allocation is a forward-thinking strategy that prepares your organization for an uncertain future. Instead of committing all resources to a single forecast, this method involves developing several plausible future scenarios and distributing resources to maintain flexibility. It is one of the most dynamic resource allocation strategies for navigating volatility.
Pioneered by Royal Dutch Shell, this approach is about preparing for multiple outcomes. For example, a pharmaceutical company might allocate its R&D budget across different disease progression scenarios, ensuring it has a viable pipeline no matter what happens.
How to Implement in Excel
Effective implementation requires developing distinct scenarios and creating a flexible resource plan in Excel.
- Develop Scenario Worksheets: Create separate worksheets for 3-5 scenarios (e.g., "Best Case," "Worst Case," "Aggressive Growth"). In each, model the resource needs (budget, staff) for that scenario.
- Use Excel's Scenario Manager: Use the built-in Scenario Manager (under Data > What-If Analysis) to define your different scenarios and switch between them easily. This allows you to see the impact of each future on your overall budget.
- Automate Analysis with AI: Ask an AI tool to find common threads: "Compare the resource plans for the 'Best Case' and 'Worst Case' scenarios and identify the 'no-regret' investments that are required in both." This helps prioritize foundational allocations.
To enhance this strategy, learn more about business forecasting methods to build more robust scenarios.
The video above provides a deeper look into the principles of scenario planning, illustrating how to think structurally about uncertain futures.
10. Value Stream Resource Allocation
Value Stream Resource Allocation is a lean methodology that organizes resources around the end-to-end activities required to deliver value to a customer. Instead of funding isolated departments, this strategy allocates capital and talent to dedicated, cross-functional teams that own a complete value stream. This aims to optimize flow and reduce wasteful handoffs.
This strategy, rooted in lean principles, shifts the focus from departmental efficiency to the speed of value delivery. For example, a bank might organize teams not by function (marketing, IT) but around a customer journey like "obtaining a mortgage."

How to Implement in Excel
Adopting this strategy requires a shift from traditional siloed thinking, which can be modeled and managed in Excel.
- Map Your Value Streams: Use Excel's SmartArt graphics or simple shapes to visually map the entire process from customer request to delivery. This exercise helps expose bottlenecks and non-value-added activities.
- Create Value Stream Budgets: Instead of departmental budgets, create budget worksheets for each value stream (e.g., "Mortgage Application Value Stream"). Consolidate all associated costs—staff, technology, marketing—into this single view.
- Use AI for Flow Metrics: Track key metrics like lead time and cycle time in an Excel table. Ask an AI tool to analyze this data: "Create a control chart for the 'Mortgage Application' lead time data and highlight any periods of unusual delay."
This visual represents how resources are organized to serve a continuous flow of value. By funding the team and not the project, organizations can respond more quickly to changing customer needs.
Resource Allocation Strategies Comparison Table
| Resource Allocation Method | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Priority-Based Resource Allocation | Medium – requires regular reassessment and stakeholder input | Moderate – clear criteria and scoring systems | Clear prioritization delivering critical initiatives first | Limited resources, strategic objectives, defined project portfolios | Aligns resources to strategic goals; transparent; reduces ambiguity |
| Agile Resource Allocation | High – iterative cycles, continuous feedback needed | High – cross-functional teams, stakeholder engagement | Highly adaptable, rapid response to changes | Fast-paced industries, software development, high uncertainty environments | Flexibility, frequent optimization, early issue detection |
| Zero-Based Resource Allocation | Very High – comprehensive justification each cycle | Very High – detailed analysis and extensive documentation | Eliminates waste, promotes efficiency and accountability | Cost optimization, legacy inefficiency, financial constraint periods | Drives cost-cutting, innovation, accountability |
| Portfolio Management Resource Allocation | High – sophisticated analysis and balancing required | High – data-intensive, requires executive oversight | Balanced investment across diverse projects, risk/return optimized | Large organizations, multi-initiative environments, innovation-focused | Enterprise-wide view, strategic alignment, data-driven decisions |
| Capacity-Based Resource Allocation | Medium to High – real-time tracking, frequent updates | Moderate to High – requires accurate capacity data | Prevents overload and burnout, improves predictability | Service orgs, consulting firms, project-based businesses | Prevents overallocation, optimizes utilization, early gap identification |
| Strategic Resource Allocation (Top-Down) | Medium – centralized with clear governance | Moderate – executive-driven resource pools | Strong strategic alignment, unified direction | Hierarchical organizations, strategic transformations, clear leadership | Clear accountability, strategic focus, reduced duplication |
| Dynamic Resource Allocation (Market-Based) | Very High – complex systems, market mechanisms needed | High – requires governance and transaction management | Responsive, efficient, autonomous resource distribution | Large decentralized orgs, entrepreneurial culture, diverse business units | Encourages competition, reveals true value, fosters innovation |
| Constraint-Based Resource Allocation (TOC) | Medium – requires accurate constraint identification | Moderate – focus resources on bottlenecks | Maximizes throughput, rapid improvements | Manufacturing, supply chain, project management with clear bottlenecks | Clear focus, prevents waste, improves system performance |
| Scenario-Based Resource Allocation | High – multiple scenario development and monitoring | High – scenario planning resources and monitoring | Builds resilience and flexibility, reduces risk | High uncertainty, long planning horizons, capital-intensive industries | Enables adaptation, balances commitment and flexibility |
| Value Stream Resource Allocation | High – requires organizational restructuring | High – cross-functional teams and training | Maximizes customer value, reduces waste, optimizes flow | Manufacturing, process-driven industries, lean/agile transformations | Breaks silos, improves flow, aligns with customer outcomes |
From Strategy to Action: Your Next Step in Resource Mastery
You now have a comprehensive toolkit of ten powerful resource allocation strategies, each adaptable for use in Excel. We have moved beyond theory, providing actionable steps and AI-powered tips to solve real-world business challenges. The common thread connecting them all is the need for clarity, strategic alignment, and the ability to adapt to changing priorities using data-driven tools.
Mastering these strategies in Excel is no longer just an operational advantage; it's a critical competitive differentiator. Effective resource allocation directly impacts your ability to innovate faster and maximize the return on every dollar spent. The key is to choose a model that aligns with your organization's goals and start implementing it in a structured, data-centric way.
Turning Knowledge into Impact with Excel and AI
The journey from understanding these concepts to implementing them successfully requires a shift in both mindset and tooling. The most successful teams treat resource allocation as a dynamic process managed within a flexible tool like Excel, enhanced with AI.
Here are the essential takeaways to put into action:
- Start with Alignment: Before selecting a strategy, ensure every resource decision is tied directly to a clear business objective within your model.
- Embrace Iteration: Perfection is the enemy of progress. Use your Excel models to build feedback loops, review allocations regularly, and adjust based on real-time data.
- Leverage Data, Not Just Intuition: Your decisions are only as good as the data supporting them. Use real-time capacity data, performance metrics, and AI-driven analysis to guide your choices.
- Empower Your Team: Resource allocation isn't just a top-down mandate. Involving team members in the process fosters ownership and uncovers valuable on-the-ground insights.
Ultimately, the goal is to create a resilient system that can absorb shocks and pivot toward new opportunities. The right combination of strategy and technology makes this possible. By moving resource management from a static exercise to a fluid, data-driven conversation in Excel, you transform it from a chore into a strategic weapon.
Ready to supercharge your resource planning in Excel? Stop spending hours on manual data crunching and start getting instant, AI-powered insights with Elyx.AI. Transform your complex spreadsheets into clear, actionable allocation models and visualizations by simply asking questions in plain English, directly within your worksheet. Try Elyx.AI for free and make smarter resource allocation decisions in a fraction of the time.
Reading Excel tutorials to save time?
What if an AI did the work for you?
Describe what you need, Elyx executes it in Excel.
Try 7 days free