A Guide to Business Forecasting Methods in Excel

Business forecasting methods are the tools companies use to make smart, data-driven predictions about the future. Think of them as your company's GPS for strategic planning. By using a mix of historical data and expert judgment—often right within a tool like Excel—you can build a reliable roadmap for everything from stocking your shelves to setting your annual budget.
What Are Business Forecasting Methods
At its heart, business forecasting is about making calculated predictions based on what you already know. It's not a crystal ball—it won’t give you a perfect picture of the future. The real goal is to reduce uncertainty so you can make better, more strategic decisions today.
This practice has come a long way. Early on, forecasting was mostly about gut feelings. Now, it's a much more scientific, data-driven game, and tools like Excel have made it accessible to everyone. We've moved from purely qualitative guesses to sophisticated quantitative models and even artificial intelligence. For instance, time series analysis has been a staple since the early 20th century, and more advanced models like ARIMA can predict demand with impressive accuracy margins, often hitting between 80-95%.
Spending too much time on Excel?
Elyx AI generates your formulas and automates your tasks in seconds.
Try for free →The Two Pillars of Forecasting
Every forecasting technique you'll encounter falls into one of two main camps: qualitative or quantitative. Understanding the difference is the first step in picking the right approach for your business.
The infographic below breaks down this fundamental structure perfectly.
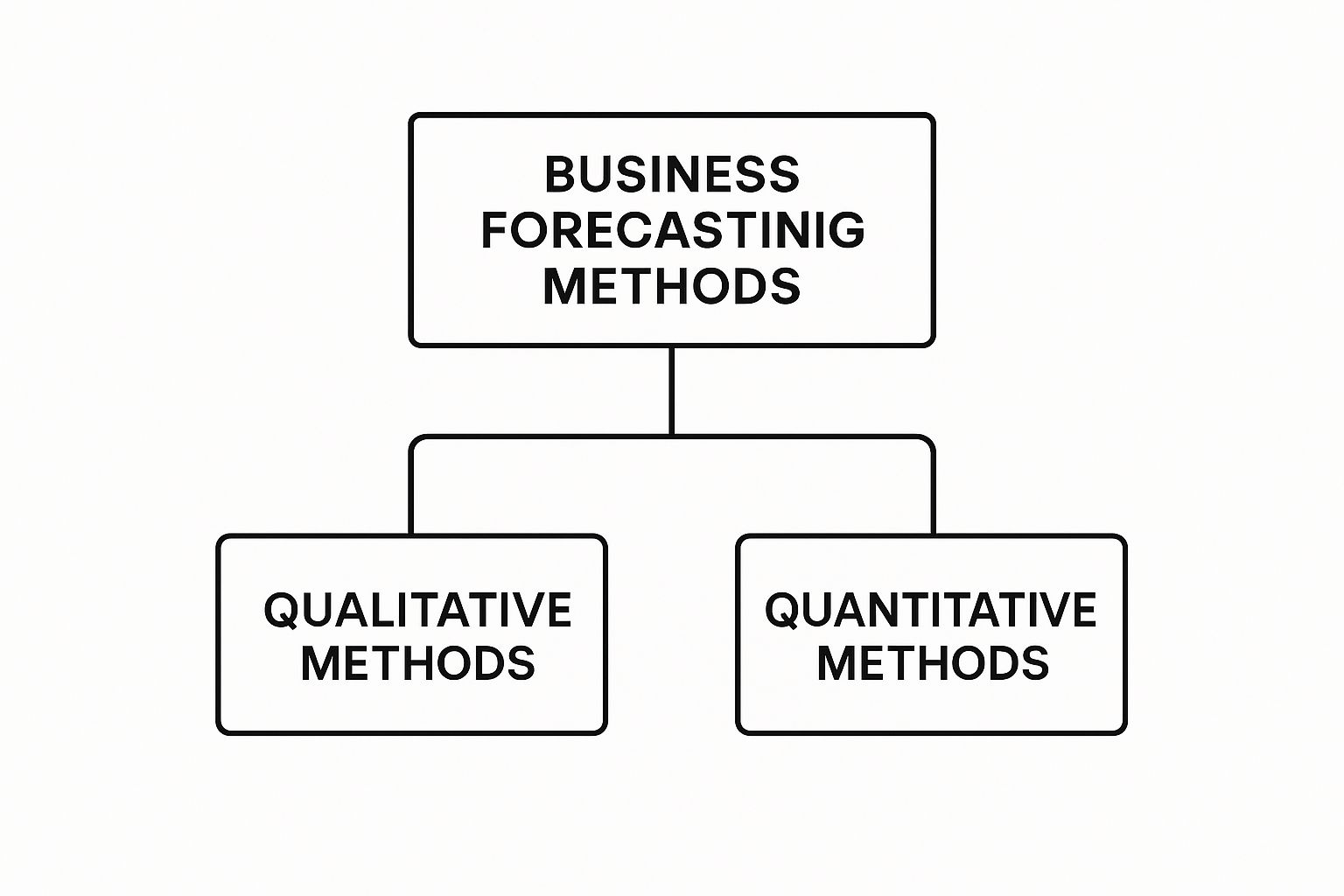
As you can see, every method has its roots in either human judgment (qualitative) or hard numbers (quantitative).
Let’s quickly break down what defines each one:
- Qualitative Forecasting is all about human expertise. It leans on the opinions of seasoned experts, customer feedback, and market intelligence. This approach is your best bet when you have little to no historical data, like when you're launching a brand-new product or exploring an unfamiliar market.
- Quantitative Forecasting is purely about the numbers. It uses past numerical data and statistical models to project future outcomes. If you have a solid history of data in your spreadsheets and your market is relatively stable, this is the way to go.
Qualitative vs Quantitative Forecasting at a Glance
Choosing between these two approaches can feel tricky, but it really comes down to what you’re trying to predict and what kind of information you have available. This table offers a side-by-side comparison to help clarify when to use each one.
| Attribute | Qualitative Methods | Quantitative Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Core Approach | Based on expert opinions, intuition, and judgment. | Based on historical data and statistical models. |
| Best For | New products, new markets, or when data is scarce. | Stable conditions with plenty of historical data. |
| Common Examples | Market research, Delphi method, expert panels. | Moving averages, regression, time series analysis in Excel. |
| Limitations | Can be subjective and prone to bias. | Can't account for sudden market shifts or unforeseen events. |
Ultimately, many businesses find the most success by blending both methods, getting the best of both worlds—the art and the science of prediction.
To see how forecasting fits into the bigger financial picture, it's worth understanding the key differences between a forecast and a budget. This guide on Budget vs Forecasting explains it well. And thanks to modern tools like Excel and AI plugins, both qualitative and quantitative forecasting are easier than ever for businesses of all sizes to implement. To learn more about putting your numbers to work, check out our guide on small business data analysis.
Using Qualitative Methods for Forecasting
While numbers tell a powerful story, they don’t always tell the whole story. This is where qualitative forecasting comes in, acting as your guide when historical data in Excel is thin, unreliable, or just plain missing.
Think about it. What if you're launching a truly innovative product or breaking into a brand-new market? You can't look back at last year's sales figures because they don't exist. In these moments, your best asset is the "human element"—the gut feelings, deep experience, and informed opinions of people who know the landscape inside and out.

Qualitative methods swap statistical formulas for structured judgment. Instead of just crunching numbers, you're gathering and making sense of opinions, survey results, and expert consensus to paint a picture of what's ahead. This approach is absolutely critical for long-term strategic planning and navigating murky, uncertain futures.
The Delphi Method Explained
One of the most tried-and-true qualitative techniques is the Delphi Method. It’s cleverly designed to build a reliable consensus from a group of experts while neatly sidestepping the dangers of groupthink, where a few loud voices can drown out everyone else.
The process is anonymous and carefully structured:
- Pick Your Panel: First, you bring together a diverse group of experts from inside and outside your company.
- Round One: A neutral facilitator sends out an anonymous questionnaire. It asks for their predictions on a specific question, like, "When do you think our new app will hit 1 million users?"
- Summarize and Share: The facilitator gathers all the answers, summarizes them, and sends the anonymous summary back to the entire panel.
- Refine and Repeat: Now, the experts get to see what their peers think. They can stick with their original forecast or revise it based on the new information. This cycle repeats a few times.
Through this back-and-forth process, the range of predictions usually gets smaller and smaller, eventually zeroing in on a single, well-thought-out consensus. A tech startup might use this with industry analysts to forecast the adoption rate for new software, landing on an estimate that’s far more reliable than one person's shot in the dark.
Market Research and Expert Panels
The Delphi Method isn't the only tool in the qualitative toolbox. Market research is another fundamental piece of the puzzle. Using surveys, focus groups, and one-on-one customer interviews, you can get a direct read on what your customers are thinking and planning to buy. It helps you understand the "why" behind their future actions.
Expert panels are a more straightforward version of the Delphi Method. You simply get a group of specialists in a room (or a video call) to discuss their views and work toward a forecast together. It’s faster, but also more open to personal biases and dominant personalities.
The real magic happens when you use these human-centric methods to enrich your quantitative analysis, not replace it. By bringing structured expert opinion into the mix, you build a more robust and resilient forecast that sees the things numbers alone can't.
How to Use Quantitative Forecasting in Excel
This is where your data comes to life. While qualitative methods rely on human expertise, quantitative forecasting lets the numbers do the talking. Using a tool you already know—Excel—you can turn your historical data into a powerful tool for predicting what's next.
Think of it this way: Excel can be more than just a digital ledger. It's a launchpad for creating data-driven projections that can genuinely shape your business strategy, without needing to be a data scientist.
The core idea behind quantitative methods is simple: what happened in the past often holds clues about the future. By digging into your numerical data—sales figures, website traffic, customer sign-ups—you can spot patterns. The good news is that Excel has tools built right in to make this analysis much easier, so you can start forecasting today.
Understanding Time Series Analysis
The most common starting point for quantitative forecasting in Excel is Time Series Analysis. This is just a fancy way of saying you’re looking at data points collected over time. It's like watching a movie of your business performance, frame by frame, to see where the plot is heading.
To do this right, you need to look for two key things in your data:
- Trends: This is the big-picture direction. Is your data generally climbing, dipping, or staying flat over the long haul? For an e-commerce shop, a trend might be a steady 5% increase in sales month after month.
- Seasonality: These are the predictable ups and downs that happen like clockwork. The classic example is a retailer seeing a huge sales spike every December for the holidays. It's a repeating, reliable pattern.
Once you can separate these predictable movements from the random day-to-day noise, you get a much clearer picture of what’s likely coming down the pipeline.
Moving Averages: A Simple Smoothing Technique
One of the most straightforward business forecasting methods you can use in Excel is the Moving Average. Its main job is to smooth out all the random bumps and dips in your data so you can see the real trend underneath.
Imagine your weekly sales data looks like a jagged, spiky mountain range. A moving average essentially sands down those sharp peaks and deep valleys into gentle, rolling hills, making the overall direction much easier to follow.
How to do it in Excel: A 3-period moving average takes the average of the last three data points to predict the next one. If your sales numbers are in column B, the formula in cell C4 would be
=AVERAGE(B2:B4). You can then drag this formula down to apply it to the rest of your data. This is a fantastic tool for simple, short-term forecasts in a relatively stable business.
Exponential Smoothing: Weighting What Matters Most
A simple moving average treats all your past data as equally important. Exponential Smoothing, on the other hand, is a bit more sophisticated. It gives more weight to your most recent data, working on the assumption that what happened last week is a better clue for next week than what happened a year ago.
This makes it much more responsive to recent changes. If your sales suddenly shot up last month because of a great marketing campaign, exponential smoothing will give that recent success more credit.
How to do it in Excel: Excel's own Forecast Sheet tool (found under the
Datatab) uses an advanced version of this method. Simply select your historical data (dates and values), clickData > Forecast Sheet, and Excel will automatically generate a forecast chart, complete with confidence intervals. It’s a powerful feature that requires zero formulas.
Regression Analysis: Connecting the Dots
So what happens when your sales are influenced by more than just the passage of time? This is where Regression Analysis becomes your best friend. It helps you uncover the relationships between one thing you want to predict (like sales) and other factors that might be driving it (like your ad budget or website traffic).
A regression model can help you answer critical questions like, "For every extra $100 we spend on Google Ads, how much do our sales typically increase?" By putting a number on these relationships in Excel, you can build a forecast based on the specific actions you plan to take.
These kinds of statistical methods are the bedrock of modern supply chain management and sales planning. In fact, companies that use techniques like regression analysis have reported cutting inventory costs by around 15-25% and reducing stockouts by up to 30%. For something even more complex, like modeling a range of possible outcomes, learning about the Monte Carlo simulation can be a real game-changer.
Using AI for Smarter Forecasting in Excel
Traditional forecasting methods in Excel are reliable, but they have their limits. They can sometimes miss subtle patterns, struggle with multiple influencing factors at once, or take too long to adapt when the market suddenly shifts. This is where Artificial Intelligence comes in, turning your spreadsheet from a simple number-cruncher into a truly predictive tool.
Think of AI and Machine Learning models as a team of super-analysts working inside Excel. They’re built to find complex relationships in your data that are almost impossible for a person to spot. They can sift through thousands of data points in seconds, uncovering hidden seasonal effects and surprising connections between variables. The result? A much more accurate and insightful forecast.
Why AI Changes the Game for Forecasting
AI takes your forecasting to the next level by handling all the heavy lifting. Instead of you spending hours trying to figure out which marketing campaign or economic indicator is really driving sales, an AI model can test countless combinations and instantly pinpoint the most important factors.
Imagine a retail manager trying to forecast demand for thousands of different products. It would be impossible to manually account for every little thing that affects sales—holidays, local events, a new marketing push, or even what a competitor is doing. An AI-powered tool can analyze all of these moving parts at once to create a precise forecast for every single item, right inside your spreadsheet.
This move from manual guesswork to automated insight is a big deal. Systematic forecasting methods (SFMs), which combine smart algorithms like AI with human expertise, are proven to boost accuracy. While over 25% of companies still rely on judgment alone, those that adopt SFMs have seen their forecast accuracy jump by 20-30%. You can dig into the research on how SFMs are changing business forecasting.
Bringing AI Directly into Your Spreadsheets
The idea of running AI models probably sounds complex. But that’s not true anymore. A new wave of AI-powered Excel add-ins has put this powerful technology right inside the familiar grid of your spreadsheet, making it accessible to anyone.
These tools do all the complicated work behind the scenes. You just need to provide the data, and the AI handles the rest. It means you can get all the benefits of advanced forecasting without writing a single line of code.
One of the easiest ways to get started is with tools designed to work directly within your worksheet. For a closer look at how these integrations work, check out our detailed guide on using AI for Excel.
How Elyx.AI Makes Advanced Forecasting Simple
Tools like Elyx.AI are designed to close the gap between complex data science and everyday business questions. It plugs directly into Excel, letting you run powerful forecasts with simple, conversational commands.
Forget about building complex formulas or trying to remember which forecasting model to use. You can just ask a question. For instance, you could highlight your past sales data and tell the AI, "Forecast sales for the next six months, and make sure to account for seasonality and our recent marketing spend."
In response, Elyx.AI gets to work and will:
- Find the Patterns: It automatically spots underlying trends and any recurring seasonal cycles in your numbers.
- Analyze Your Variables: The model figures out the relationships between sales and other factors you provide.
- Generate a Forecast: It gives you a clear, data-driven forecast, often with charts and confidence intervals to show you the likely range of outcomes.
This approach finally makes advanced business forecasting methods practical for everyone. It removes the technical roadblocks, so you can stop wrestling with formulas and start focusing on what the numbers mean for your business. You get to spend your time making smarter decisions, backed by more reliable predictions.
How to Choose the Right Forecasting Method
So, you've got a whole menu of forecasting methods in front of you, from simple Excel formulas to sophisticated AI models. The big question is, which one do you pick? The secret isn't finding the one "best" method—it's about picking the right tool for the job you need to do right now.
Think of it like choosing a vehicle. You wouldn't take a sports car off-roading, and a monster truck is overkill for a trip to the grocery store. In the same way, your forecasting method needs to match your data, how far into the future you're trying to see, and how precise you need to be.

Key Factors in Your Decision
Before you open Excel, ask yourself three key questions. Your answers will steer you toward the perfect forecasting approach for your specific situation.
- What Does Your Data Look Like? This is the most important piece of the puzzle. If you’re sitting on years of clean, consistent sales data, you’re in a great position to use quantitative methods. But if you're launching a brand-new product with zero history, you’ll have to rely on qualitative insights instead.
- What Is Your Time Horizon? Are you trying to figure out what’s happening next week or five years from now? Short-term predictions, like figuring out weekly staffing, work well with simple time-series models like Moving Averages. Long-term strategic planning, on the other hand, demands a mix of trend analysis and expert opinion to navigate all the uncertainty.
- How Accurate Do You Need to Be? The stakes matter. Forecasting your budget for the next quarter requires a high level of accuracy, making a powerful AI model in Excel a smart move. But if you just need a ballpark estimate for an internal marketing goal, a quick historical growth calculation might be all you need.
The core principle is to match the complexity of the method to the complexity of the problem. Over-engineering a simple forecast wastes time, while under-powering a critical one introduces unnecessary risk.
Matching the Method to the Mission
Let's make this more concrete. The decision-making guide below connects common business needs with the most effective business forecasting methods you can use right in Excel, helping you see how these factors come into play.
Which Forecasting Method Should You Use?
This table will help you choose the most appropriate forecasting method based on common business scenarios and the data you have on hand.
| Business Scenario | Data Availability | Best Method(s) | Why It Works |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weekly Inventory for a Retail Store | High (years of sales data) | Moving Average or Exponential Smoothing | Perfect for short-term, stable demand. These methods smooth out random noise to reveal the immediate trend in Excel. |
| Quarterly Sales for an Established Product | High (stable historical data with seasonality) | Excel's Forecast Sheet or AI Model (Elyx.AI) | These tools automatically detect seasonality and complex patterns, providing a more accurate forecast than simpler methods. |
| Annual Revenue for a New Startup | Low to None | Qualitative (Market Research, Delphi Method) | With no historical data, expert opinion and customer intent are the only reliable sources for making an educated guess. |
| Five-Year Strategic Growth Plan | Mixed (some historical, high uncertainty) | Hybrid (Regression + Qualitative judgment) | Regression in Excel can project trends, but expert judgment is needed to adjust for market shifts and strategic pivots. |
As you can see, the right method really depends on the context of the problem you're trying to solve.
The Power of a Hybrid Approach
You don't have to be a purist and stick to just one method. In fact, some of the most accurate forecasts come from mixing and matching. A hybrid approach lets you combine the hard numbers from a quantitative model with the real-world smarts that only human experts have.
For example, you could use an AI tool like Elyx.AI to generate a baseline sales forecast in Excel. Then, bring that forecast to your sales team. They can provide on-the-ground intelligence about upcoming deals, what competitors are doing, or how customers are feeling.
This combination gives you the best of both worlds: the mathematical rigor of a model and the street-smart insights of your team.
So, What's Next? Putting Your Forecasts to Work
We've walked through a lot, from gut-feel predictions to AI models you can use right in Excel. The big takeaway? Business forecasting isn't some dark art reserved for data scientists. It’s a practical tool that can give you a real advantage, turning your historical data from a dusty archive into a roadmap for the future.
You've seen the whole landscape—from the wisdom-of-the-crowd approach of qualitative methods to the hard-number crunching of quantitative models. The journey shows a clear path from looking in the rearview mirror to using AI to see what’s around the corner.
Stop Reacting and Start Planning
Ultimately, this is all about shifting from being reactive to being proactive. Instead of just responding to what the market throws at you, you can start making moves that shape your own success. And you don't need a Ph.D. in statistics to get started. It can begin with a simple formula in a spreadsheet and grow from there.
The real magic of forecasting isn’t about hitting a perfect number. It's about understanding the why behind the numbers. This lets you ask better questions, put your money and people where they matter most, and walk into an uncertain future with a lot more confidence.
Taking That First Step
Every big strategic shift starts with one small, concrete action. With so many methods to choose from, there's a perfect starting point for you, no matter how much data you have or how comfortable you are with spreadsheets.
Ready to make your move? Here’s how to get going:
- Pick One Method: Don't try to boil the ocean. Start with something simple that solves an immediate problem. A Moving Average for inventory or using the Forecast Sheet tool for sales are great places to begin.
- Tackle a Real Problem: Theory is nice, but results are better. Apply the method to a real-world business challenge you're facing right now, like figuring out sales targets for next quarter or deciding how to split up your marketing budget.
- Learn as You Go: Your first forecast will probably be wrong. That’s not just okay; it's expected. The goal is to learn from it, tweak your approach, and slowly build a habit of making decisions based on data, not just hunches.
By taking that first step, you start a powerful chain reaction. You begin turning your data from something that just sits there into your single most valuable asset for building a successful future.
Got Questions? We've Got Answers
Diving into business forecasting can bring up a few questions. We've tackled some of the most common ones here to help you get started with confidence.
What’s the Most Accurate Forecasting Method?
This is the million-dollar question, but the honest answer is: it depends. There's no single magic bullet that works for every business, every time. The right method really comes down to your specific situation and the kind of data you're working with.
If you have years of solid, stable sales data, quantitative methods like Exponential Smoothing (via Excel's Forecast Sheet) or an AI model can give you incredibly precise short-term predictions. But if you're launching a brand-new product, a qualitative method like the Delphi Method, which pools expert opinion, will give you a much more realistic forecast.
The secret weapon for accuracy is often a hybrid approach. By combining the hard numbers from a statistical model in Excel with the real-world insights of your experienced team, you get a forecast that’s both data-driven and reality-checked.
How Often Should I Update My Forecasts?
Your update schedule should mirror the pulse of your business. A one-size-fits-all answer just doesn't work here; it’s all about matching the speed of your industry.
For a fast-paced retail or e-commerce business, things change quickly. Monthly or even weekly updates are pretty standard to keep on top of inventory and marketing. On the other hand, if you're in B2B software with long sales cycles, a quarterly forecast is often more than enough for solid strategic planning. The goal is to set a regular rhythm and be ready to adjust whenever something big happens—like a new competitor or a market shift—that could throw your numbers off.
Can I Do Real Forecasting in Excel Without a Data Science Degree?
Yes, you absolutely can. While old-school statistical modeling in Excel can feel like learning a new language, modern tools have brought powerful forecasting to the rest of us.
Excel’s built-in Forecast Sheet is a great starting point and can generate a solid forecast from your time-series data with just a few clicks. For even more muscle, AI-powered add-ins like Elyx.AI are built for business pros, not data scientists. They let you run complex models just by typing what you want in plain English. You can ease into it and add these tools as you get more comfortable.
Ready to stop guessing and start forecasting with confidence? Elyx.AI plugs directly into Excel, putting powerful, AI-driven forecasts at your fingertips with simple commands. Turn your spreadsheet into a predictive powerhouse and start making smarter, data-backed decisions today. Start your free trial at getelyxai.com.
Reading Excel tutorials to save time?
What if an AI did the work for you?
Describe what you need, Elyx executes it in Excel.
Try 7 days free