How to Automate Excel: 7 Methods That Save Hours Every Week

Learning how to automate Excel is really about reclaiming your most valuable asset—time. It's about taking those mind-numbing, repetitive data tasks off your plate for good. You can do this by using Excel’s own built-in tools, like VBA and Power Query, or by exploring modern solutions like Office Scripts and AI add-ins.
This guide will walk you through each of these powerful methods. My goal is to give you the practical knowledge you need to pick the right tool for the job and start automating today.
Why Excel Automation Is Your New Superpower
Let's be real. Manually copying, pasting, formatting, and consolidating data day after day is a major drain. It’s not just tedious; it's a roadblock that keeps you from the high-impact, strategic work you were actually hired to do. Mastering Excel automation completely changes this dynamic.
Spending too much time on Excel?
Elyx AI generates your formulas and automates your tasks in seconds.
Try for free →This isn't just about "saving time," though. It's about fundamentally transforming your entire workflow. You go from being someone who just uses spreadsheets to someone who architects intelligent, efficient processes. The point isn't to become a programmer overnight. It's about making Excel work for you, not the other way around.
We'll focus on four key methods to get you there:
- VBA Macros: The classic, powerhouse tool for automating complex and highly customized tasks right on your desktop.
- Power Query: Your go-to for anything related to data cleaning and transformation. You can build repeatable "recipes" to clean messy data with a single click.
- Office Scripts: The modern, cloud-based successor to VBA. It's perfect for automating tasks in Excel for the web and integrating with other Microsoft 365 apps.
- AI Tools: The next frontier. Use plain English to generate formulas, create summaries, and build entire workflows without needing deep technical skills.
Finding the Right Automation Tool
The best tool for you depends entirely on what you're trying to accomplish. Are you cleaning data? Repeating the same clicks over and over? This decision tree is a great starting point for matching your task to the right method.
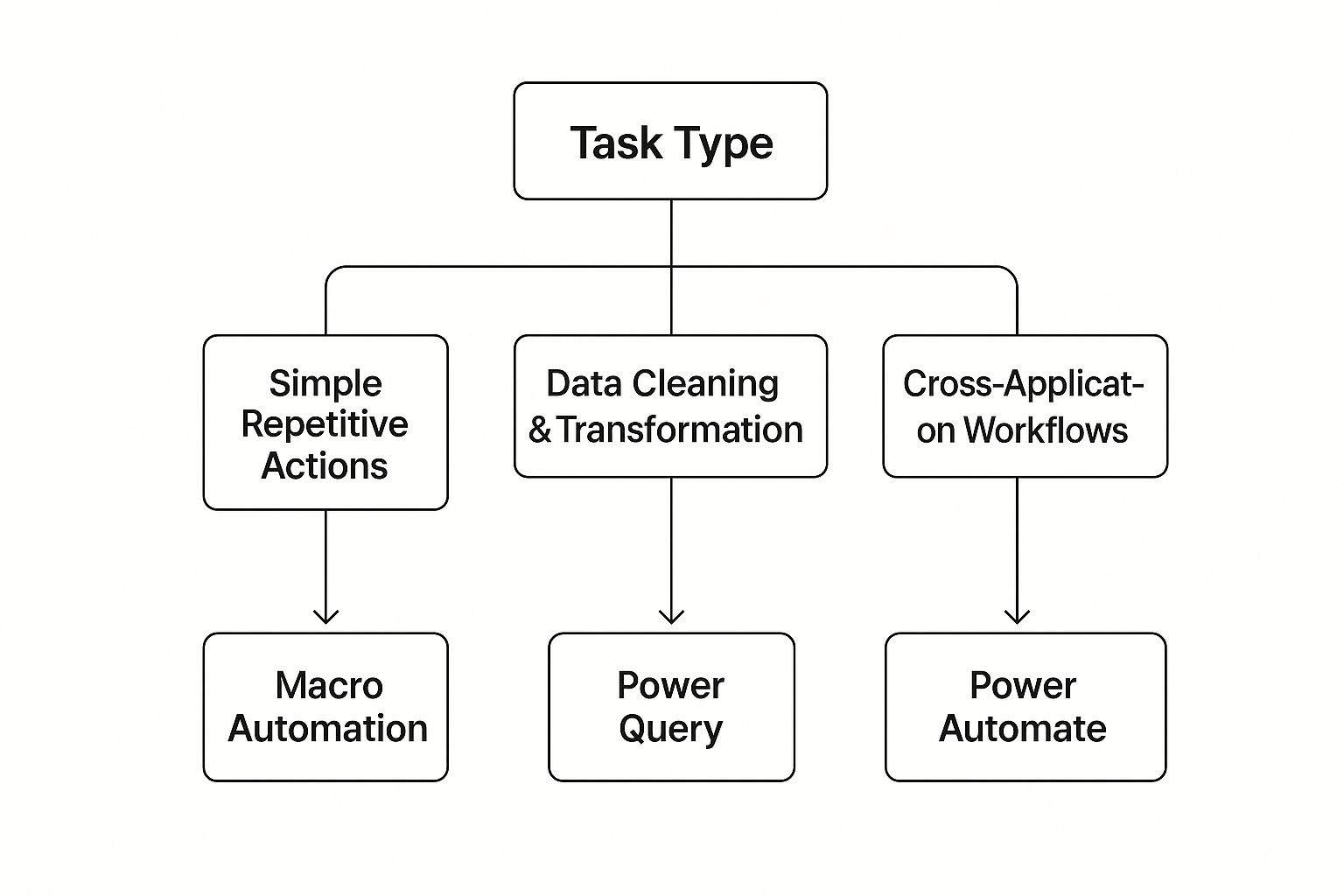
As you can see, the choice becomes pretty clear. If you're stuck in a loop of repetitive clicks, a macro is your best friend. For heavy-duty data cleanup, Power Query is the champion. And if your workflow needs to connect with other apps, Power Automate is the way to go.
Choosing Your Excel Automation Method
To help you decide at a glance, here’s a quick comparison of the primary Excel automation methods. Think about what you need to do and what skills you already have (or are willing to learn).
| Method | Best For | Required Skill Level | Platform |
|---|---|---|---|
| VBA Macros | Complex, repetitive tasks and custom user interfaces (UI). | Intermediate to Advanced | Desktop Only |
| Power Query | Cleaning, transforming, and combining data from multiple sources. | Beginner to Intermediate | Desktop & Web |
| Office Scripts | Cloud-based automation and integration with Power Automate. | Intermediate (JavaScript) | Web Only |
| AI Add-Ins | Generating formulas, summaries, and simple automations with text prompts. | Beginner | Desktop & Web |
Each tool has its place, and often, the most powerful solutions come from knowing how to combine them. Start with the one that solves your most immediate pain point.
The True Impact of Automation
This move toward automation is much more than a trend; it's a fundamental shift in how productive work gets done. By 2025, the industrial automation market is projected to hit $227 billion, a number driven by the incredible value it creates.
The proof is in the results. Over 90% of workers say automation makes them more productive, and companies see an average 22% reduction in operating costs. Technologies like Robotic Process Automation (RPA)—which closely mirror the workflows you can build in Excel—often deliver an ROI between 30% and 200% in the first year alone. You can learn more about these automation statistics and their business impact.
Key Takeaway: Getting skilled in Excel automation isn't just about boosting your own efficiency. It aligns your abilities with a top business priority: cutting down on manual work to free up time for smart analysis and better decision-making.
Automating Repetitive Tasks with VBA Macros
When you need to truly automate Excel, Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) is the original workhorse, and for good reason. It’s a powerful scripting language built right into Excel, giving you an incredible level of control over every single part of your workbook. Think of it as giving precise, repeatable instructions to a super-efficient assistant who never gets tired and never makes a typo.
VBA is at its best when you’re dealing with complex, multi-step tasks that you have to do over and over again. Imagine getting a messy sales report every month. It always has inconsistent formatting, extra columns you don’t need, and requires a handful of calculations before it’s useful. Doing that by hand isn't just boring; it's a perfect recipe for errors. With a VBA macro, you can distill that entire cleanup process down to a single click.
First, You Need the Developer Tab
Before you can record macros or start writing any code, you have to enable the Developer tab in Excel. It's hidden by default, but getting it turned on is a simple, one-time setup.
- Head to File > Options.
- In the Excel Options window, click on Customize Ribbon.
- Look to the right side under Main Tabs and just check the box next to Developer.
- Click OK.
You’ll now see the Developer tab sitting in your Excel ribbon. This is your new command center for all things automation, giving you access to the Macro Recorder, the VBA Editor, and other handy controls.
Your First Automation: The Macro Recorder
The absolute easiest on-ramp to automating Excel with VBA is the Macro Recorder. This fantastic tool literally watches your actions—every click, every formula, every format change—and translates them into VBA code for you. It's an incredible learning tool that builds the foundation for your first scripts.
Let's go back to our messy sales report scenario. Say you want to automate these steps:
- Delete columns B and F (which contain junk like "Internal ID" and "Notes").
- Apply a currency format to the "Revenue" column.
- Add a new column called "Profit Margin" that calculates a simple formula.
- Make the header row bold and give it a nice background color.

To record this, jump over to the Developer tab and click Record Macro. Give it a descriptive name (something like Format_Monthly_Report) and then just perform all the steps exactly as you would manually. When you're done, click Stop Recording. That's it—you've just created your first piece of automation!
From Recorded Code to a Flexible Script
The code you get from the Macro Recorder is a great start, but it's often very rigid. It records specific cell ranges, like A1:G50, which won't work if next month's report has 100 rows instead of 50. This is where the real power of VBA shines—you can edit the code to make it flexible and, dare I say, intelligent.
To see what you've created, go to the Developer tab and click Visual Basic. This opens the VBA Editor, where you'll find your recorded macro tucked away in a "Module." It might look a little intimidating at first, but you'll quickly start to recognize patterns that line up with the actions you took.
Pro Tip: Don’t be afraid to experiment in the VBA Editor. The code generated by the recorder is your personal sandbox. Try changing a
Range("E2:E50")to something else and see what happens. This hands-on tinkering is the fastest way to really get how VBA thinks.
One of the first things you'll want to learn is how to make your code work on datasets of any size. Instead of a fixed range, you can use a small snippet of VBA to find the last used row in a sheet. This simple change turns a static script into a dynamic tool that adapts to your data.
' Example of finding the last row
Dim lastRow As Long
lastRow = ActiveSheet.Cells(Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row
' Now use this variable to apply formatting to the correct range
Range("D2:D" & lastRow).NumberFormat = "$#,##0.00"
This tiny tweak is a total game-changer. It tells Excel to find the last cell with data in column A and use that row number to define the range. Now, your macro will work perfectly whether your report has 50 rows or 5,000.
The Bigger Picture of Excel in Business
This level of automation is critical because Excel is still the undisputed king of business operations, especially in finance. As of early 2025, a whopping 58% of finance leaders globally still rely heavily on Excel for managing their most important processes. It's familiar and flexible, which keeps it at the heart of many workflows.
However, this heavy reliance creates real operational risks. One survey found that some companies are juggling tens of thousands of separate Excel files, which dramatically increases the chance for human error and inefficiency. Learning to automate Excel with VBA is a direct way to mitigate those risks by standardizing your processes. You can find more stats and insights from the business process automation community.
By creating robust VBA scripts, you're not just saving a few minutes here and there; you're building a more reliable and scalable system inside the tool your organization already knows and trusts. This makes your work more valuable and your processes far less prone to costly mistakes.
Effortless Data Cleanup with Power Query
If you've ever found yourself staring at a messy spreadsheet, knowing you're about to lose hours manually deleting columns, fixing weird formatting, or mashing together data from different files, then you need to meet Power Query. It's a data transformation tool built right into Excel, and frankly, it's a game-changer for data prep.
Instead of doing the same tedious cleanup tasks over and over, you essentially create a reusable "recipe." Power Query records every step, letting you automate the entire process for the next time.
This is the perfect fix for anyone who dreads month-end reporting because the source data is always a disaster. It’s brilliant at connecting to all sorts of data sources—like CSV files, other Excel workbooks, or even company databases—and letting you whip that data into a clean, analysis-ready format.
And the best part? You barely have to touch your keyboard. The interface is intuitive and records your clicks, creating a repeatable query you can refresh with a single button. This makes it a fantastic way to automate Excel without needing to learn the complexities of VBA.

A Real-World Data Cleanup Scenario
Let's imagine a common situation. You get monthly sales data from three different regional offices. Each one sends you a separate CSV file, and they are consistently messy in their own unique ways.
- The North region's file has extra "Internal Note" columns you don't need.
- The South region's file uses a "dd-mm-yyyy" date format, which is different from your standard "mm/dd/yyyy".
- The West region's file is littered with "Test Sales" rows that need to be filtered out.
Trying to combine and clean these files manually every single month is not just a time-sink; it's a recipe for mistakes. This is exactly the kind of workflow Power Query was built to automate.
Your First Power Query Automation
Getting started is surprisingly simple. You just have to point Power Query to your files.
- Head to the Data tab on the Excel ribbon.
- Click Get Data > From File > From Folder.
- Just browse to the folder holding your three regional CSVs and click OK.
Excel gives you a quick preview of the files it found. From there, you'll click Transform Data (or sometimes Combine & Transform Data). This is where the magic begins. You're now inside the Power Query Editor, your new command center for data cleanup.
You'll see a preview of your combined data. Now, look to the right-hand side for a pane called Applied Steps. Every single action you take—from removing a column to filtering a row—gets recorded here as a separate step. This list is your automation.
Key Insight: The "Applied Steps" list is the heart of Power Query. Think of it as a visual log of your entire cleaning process. You can click on any step to see what the data looked like at that stage, and you can easily tweak or remove steps without starting over.
Transforming Data with Simple Clicks
Now, let's fix the specific problems with our sales data using the Power Query Editor's point-and-click interface.
-
Removing Junk Columns: To ditch the "Internal Note" column, just right-click its header and choose Remove. Bam. A "Removed Columns" step appears in your list.
-
Standardizing Formats: For that messy "Date" column, click the little data type icon (it might look like a calendar or "ABC") in the column header. Select Date from the menu. Power Query is smart enough to figure out the different formats and unify them.
-
Filtering Out Bad Data: To get rid of those "Test Sales" rows, click the filter arrow on the column header. Uncheck "Test Sales" from the list—just like a regular Excel filter—and hit OK. A "Filtered Rows" step is now part of your recipe.
Once you’ve made all your changes, just click Close & Load. Power Query runs through all your recorded steps and loads the perfectly clean, combined data into a new table in your worksheet.
Next month, when the new CSV files arrive, you just drop them in the same folder, right-click your output table, and hit Refresh. The entire cleanup process runs automatically in seconds.
This approach is incredibly effective for data prep. To explore more advanced techniques, you can also check out our detailed guide on how to clean data in Excel. By getting comfortable with Power Query, you're not just finding a quicker way to do a task—you're building a reliable, automated system that will save you countless hours down the road.
Modern Automation with Office Scripts and the Cloud
While VBA is still a workhorse for desktop-based Excel tasks, the reality is that our work has moved online. This is where Office Scripts enter the picture, offering a modern, secure, and collaborative way to automate Excel in the cloud. Think of Office Scripts as the natural successor to VBA, built for a world where your files live on OneDrive and your team works together in real time.
Instead of the older VBA language, Office Scripts use TypeScript, a modern extension of JavaScript. This isn't just a technical detail; it means better security, improved performance, and, most importantly, the ability to run your automations anywhere you can open Excel for the web. That means Windows, macOS, or even a browser on a Chromebook—a level of cross-platform flexibility VBA just can't match.

Creating Your First Cloud-Based Script
The great thing about Office Scripts is that you don't need to be a coding guru to get started. Much like VBA's macro recorder, Office Scripts has a user-friendly Action Recorder. It watches what you do in Excel for the web and translates those clicks and keystrokes into a reusable script.
Let's walk through a common scenario. Imagine you need to set up a standardized project tracking sheet every time a new client comes on board. Instead of manually creating the same columns and formatting over and over, you can automate it once.
Head over to the Automate tab in Excel for the web and try this:
- Click Record Actions. A pane will pop up on the right, showing you the code as it's generated.
- Rename the current sheet to something descriptive, like "Project Tracker".
- Create your header columns: "Task Name," "Assigned To," "Start Date," "Due Date," and "Status."
- Apply some simple formatting. Make the header row bold and give it a fill color so it stands out.
- Use Data Validation to create a dropdown list in the "Status" column with predefined values like "Not Started," "In Progress," and "Completed."
Once you're done, click Stop. You can then save the script with a clear name, like "Create Project Tracker Sheet." From now on, whenever you need a new tracking sheet, you can run this script with a single click from the Automate tab.
The Real Power: Integration with Power Automate
Having a one-click script is nice, but the true game-changer with Office Scripts is its seamless integration with Power Automate. This is where you graduate from simple, in-sheet automation to building powerful workflows that connect multiple applications and run entirely in the cloud—even when your computer is off.
With Power Automate, you can create a "flow" that automatically runs your script based on a specific trigger. This transforms your simple script into a fully autonomous business process.
Key Takeaway: The combination of Office Scripts and Power Automate lets you connect Excel to over 1,000 other services, from SharePoint and Outlook to third-party apps like Salesforce or X.
Let's expand on our project tracker example. Say your company uses a dedicated OneDrive folder for new client contracts. We can build a Power Automate flow that does this:
- Trigger: A new file (the client contract) is added to a specific OneDrive folder.
- Action 1: Create a brand-new Excel workbook in a separate "Project Files" folder.
- Action 2: Run our "Create Project Tracker Sheet" Office Script on that new workbook.
This automated workflow guarantees that a perfectly formatted project tracker is generated the moment a new client is signed, all without anyone lifting a finger. This level of interconnectedness is what modern business is all about. We've all seen how tightly linked our tech ecosystem is—a single event can have a ripple effect, requiring massive coordination. Your automations should be just as connected to work effectively.
Setting this up in Power Automate is straightforward. You choose a trigger like "When a file is created" and then add an action for "Run script" in Excel Online. You just point the flow to your saved Office Script, and the platform takes care of the rest. This is how you automate Excel in a way that truly scales with your business.
Pushing Past Excel's Limits with Python and AI
Sometimes, you hit a wall with Excel's built-in tools. While VBA and Power Query are fantastic for a lot of automation, they have their limits. When you're dealing with truly complex data analysis, massive file operations, or integrating with external web services, you need more horsepower. This is exactly where a modern programming language like Python comes into the picture.
Data professionals are increasingly leaning on Python for its incredible versatility and raw processing power. It lets you take control of Excel files programmatically, doing things that just aren't practical with macros alone. You can manipulate huge datasets, generate intricate charts, and talk to other applications, all without ever manually opening the Excel interface.
Getting Serious with Python and Pandas
One of the cornerstones of data work in Python is a library called Pandas. If you know Power Query, think of Pandas as Power Query on steroids. It's built for high-performance data wrangling, giving you clean data structures and powerful tools to transform, analyze, and visualize your information. For those heavy-lifting Excel tasks, the Python-Pandas combo is a game-changer.
Let's walk through a real-world scenario. Say you're a financial analyst responsible for creating 150 unique performance reports for your clients every quarter. You have a massive Excel sheet with all the raw transaction data and a polished Excel template for the final report. Doing this by hand would be a nightmare—tedious, slow, and full of opportunities for mistakes.
Here’s how you could automate the entire thing with Python and Pandas:
- Load the Data: First, your script uses Pandas to pull all the raw data from your master spreadsheet into a clean, organized table called a DataFrame.
- Process and Analyze: Next, you can programmatically loop through your client list. For each one, you filter the data down to their specific metrics. This is where Python shines—you can run complex calculations like portfolio volatility or custom financial models that would be a headache to build in Excel.
- Generate the Reports: Finally, for each client, the script grabs your report template, drops in their calculated data and personalized charts, and saves it as a brand-new Excel file (e.g.,
ClientName_Q3_Report.xlsx).
That's the beauty of it. You write the logic once, and it can crank out hundreds of custom reports in minutes. A task that used to take days is now done before you finish your coffee.
The New Wave: AI Copilots and Smart Add-ins
While Python gives you the ultimate power, the newest approach to Excel automation comes directly from artificial intelligence. AI-powered copilots and add-ins are completely changing how we interact with spreadsheets by letting us automate complex work using simple, plain-English commands.
Instead of wrestling with a tangled nested formula, you can just ask a tool like Elyx.AI to "calculate the year-over-year growth for each product category." The AI will instantly generate the correct formula for you.
These AI assistants are much more than just formula writers. They can look at your data, suggest the best charts, build pivot tables, and even write entire VBA scripts based on a simple description of what you need.
For example, you could open an AI chat panel and type, "I have sales data in columns A through G. Create a pivot table showing total revenue by region and month, then make a bar chart from it." The AI can handle all of that in one go, turning a multi-step manual chore into a single, quick conversation. This completely lowers the barrier to entry for powerful automation; you no longer need to be a developer to build sophisticated workflows.
AI is also a huge help with data transformation and cleaning, which is often the most time-consuming part of any analysis. You can learn more about this in our guide to mastering data transformation in Excel.
Automation's Modern Playground
The fact that programming languages like Python are being integrated directly into Excel tells you everything you need to know about the future of spreadsheet work. Excel automation has moved beyond simple macros, and since at least 2024, Python's native presence has given users a modern environment for everything from report generation to workflow integration. You can even trigger complex Python scripts from a simple button inside your worksheet, blending Python’s powerful libraries with Excel's familiar interface.
Whether you decide to go deep with Python or embrace the intuitive power of AI, you’re tapping into a new era of productivity. These advanced methods let you offload the manual grunt work and focus on what really matters: finding strategic insights in your data.
Answering Your Top Excel Automation Questions
Once you start digging into automating Excel, you're bound to have questions. It can feel like you're trying to choose between a hammer, a screwdriver, and a power drill—they all build things, but they're for very different jobs. Let's clear up some of the most common points of confusion I see when people are getting started.
Is It Still Worth Learning VBA in 2024?
This is probably the most frequent question I hear. With all the new tools like Office Scripts and AI assistants, is VBA a dead language? Absolutely not.
VBA is still the undisputed king for heavy-duty, complex automation within the desktop version of Excel. If you need to build custom forms for user input, create intricate financial models with custom functions, or automate tasks that interact with other desktop applications, VBA gives you a level of control that nothing else can match.
However, if your work lives in the cloud and involves a lot of collaboration through Teams or SharePoint, you'll want to look at Office Scripts. It's built for the web-first world, making it a more secure and seamless fit for modern, cross-application workflows.
Power Query vs. VBA: Which One Do I Use?
People often get stuck here, but the distinction is actually pretty simple once you see it.
My rule of thumb: Power Query is for data, VBA is for actions.
Think of Power Query as your data janitor. Its entire job is to get data from all sorts of messy sources—databases, websites, other files—and clean, shape, and combine it into a perfect, usable table. It creates a repeatable recipe for all that data prep.
-
You'll want Power Query when: Your main task is importing and transforming data. Think cleaning up inconsistent date formats, merging sales data from three different regions, or unpivoting a report.
-
You'll want VBA when: You need to do something with the data once it's already in your worksheet. This means tasks like generating a PDF report, automatically emailing it to your boss, or creating custom charts based on user selections.
The most powerful workflows I've built actually use both. I'll have Power Query do the heavy lifting of pulling and cleaning the data, and then a simple VBA macro runs to analyze the fresh data and format the final report.
How Secure is Excel Automation?
Security is a huge deal, and this is where the tools really show their differences.
VBA macros can be a security headache. We've all seen that yellow "Security Warning" bar. A badly written or malicious macro can cause real damage by accessing your file system. This is why it’s critical to only ever run macros from sources you completely trust.
Office Scripts are a whole different ballgame. They run in a secure "sandbox" in the cloud, completely isolated from your local computer and network. This makes them a much safer bet for any automation you plan to share with your team or across your company.
Can AI Really Do My Excel Work for Me?
AI has definitely changed the game, but it's more of a super-powered assistant than a full replacement for tools like VBA or Power Query. Think of it as a copilot, not the pilot.
An AI add-in is brilliant for those "in-the-moment" tasks. Need a ridiculously complex formula that would take you 20 minutes to figure out on Google? Just ask the AI in plain English. Want to instantly create a pivot table or a chart from a messy data range? AI can often do it in seconds.
While AI is fantastic for speeding things up, it's still important to have a solid grasp of your data and what you're trying to achieve. For a deeper dive into that, check out our guide on how to analyze data in Excel.
The smartest approach is a hybrid one. Use the specific tool that solves your immediate problem most effectively.
Ready to bring intelligent automation directly into your spreadsheets? Elyx.AI is a powerful AI add-in that lets you generate formulas, clean data, and create summaries using simple English prompts. Stop wrestling with complex functions and start getting insights faster.
Get Started with Elyx.AI for Free
Reading Excel tutorials to save time?
What if an AI did the work for you?
Describe what you need, Elyx executes it in Excel.
Try 7 days free