Master Data Management in Excel: Your Practical Guide

When we talk about data management in Excel, we're really talking about the art of taking raw, messy information and turning it into something clean, organized, and reliable. It’s the essential groundwork that allows you to pull clear, actionable insights from your spreadsheets. Without it, you’re just making guesses; with it, you’re making confident business decisions.
Why Is Excel Still the King of Data Management?

In a world full of flashy business intelligence tools and complex databases, you might wonder why good old Excel still reigns supreme. It’s simple, really: accessibility and familiarity. For most professionals, Excel is the Swiss Army knife of data—it’s versatile, everyone knows how to use it (at least the basics), and it’s probably already on your computer.
Spending too much time on Excel?
Elyx AI generates your formulas and automates your tasks in seconds.
Try for free →This universal presence makes it the perfect first stop for data. Before information ever makes its way into a sophisticated analytics platform, it almost always lives in an Excel sheet first. Its simple grid is tangible and visual, giving you a hands-on way to organize information that more abstract systems just can't match.
The Bedrock of Solid Business Decisions
Getting data management right in Excel isn’t just about neatness. It’s about building a foundation of trust in your own information. When your data is well-managed, every subsequent step—from financial forecasting to inventory planning—is backed by confidence. The quality of your decisions is a direct reflection of the quality of your data.
This guide will walk you through the entire process, built on four fundamental pillars that turn a simple spreadsheet into a powerhouse for analysis. To give you a clear overview, here are the core principles we'll be covering.
Core Principles of Effective Excel Data Management
| Principle | Objective | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Structuring | Arrange data in a logical, consistent table format. | Allows Excel’s tools (like sorting, filtering, and PivotTables) to work seamlessly. |
| Cleaning | Find and fix errors, duplicates, and inconsistencies. | Ensures accuracy and prevents misleading analysis. |
| Validating | Set up rules to prevent incorrect data entry from the start. | Maintains data integrity over time and reduces future cleanup work. |
| Analyzing | Use Excel's functions and features to uncover trends and insights. | Turns raw data into strategic business intelligence. |
Mastering these four areas is what separates a basic user from a true Excel pro. It’s how you unlock the program's full potential.
Think of Excel as a universal language for data. It's the common ground where teams can collaborate, share insights, and build a shared understanding of business performance without needing specialized training.
Excel's Enduring Role in Business
Even with the rise of newer platforms, Excel's place in the business world is secure. Studies reveal that around 54% of businesses continue to rely on it for a huge variety of data tasks. With over 71,000 users in the United States alone using it for document and data management, its importance is undeniable. You can dig deeper into these trends by checking out the latest Excel statistics.
This guide is designed to give you practical, real-world skills. By the time you're done, you’ll see how this everyday tool can become one of your most powerful assets for achieving true data mastery.
How to Structure Your Data for Flawless Analysis
Think of your data like the foundation of a house. If it's shaky, messy, or built on uneven ground, everything you try to build on top of it—whether it's a simple chart or a complex financial model—is at risk of collapsing. Solid data management in Excel always starts with building a predictable, rock-solid structure. Without it, you'll constantly be fighting against the software instead of making it work for you.
Properly structured data is what unlocks Excel’s most powerful features, like sorting, filtering, and PivotTables. A messy, "human-readable" layout might seem intuitive at first, but it’s often completely incompatible with these automated tools. The real goal is to create a simple, machine-readable table that Excel can understand and work with instantly.
The Unbreakable Rules of Data Structure
To get your data ready for Excel's analytical engine, you have to follow a few rules. These aren't just suggestions; they are what turn a basic spreadsheet into a true database, unlocking its full potential.
- One Single Header Row: Your table needs to begin with one—and only one—header row. This row gives a unique name to each column, like "Sale Date," "Product ID," or "Region." Stacking multiple header rows or adding titles above the headers will just confuse Excel's tools.
- No Merged Cells or Blank Rows: Merged cells are the number one culprit behind sorting and filtering errors. In the same way, completely blank rows or columns will break up your dataset, tricking Excel into thinking it's at the end of the table. Every single row should represent a complete record.
- Consistent Data Types in Columns: Each column must contain only one type of data. A "Sale Date" column should only hold dates, and a "Revenue" column should only hold numbers. Mixing text, numbers, and dates in the same column is a recipe for disaster when it comes to calculations and analysis.
Why This Structure Is So Critical
Following these rules isn't just about being tidy; it's about making Excel actually work. When your data is structured as a proper table, Excel sees it as a coherent dataset. This is what allows you to instantly apply filters, sort by any column, and, most importantly, create dynamic PivotTables to summarize millions of records in seconds.
For example, have you ever tried to create a PivotTable from a spreadsheet with merged header cells? It almost always throws an error. The tool simply can't figure out which fields it's supposed to be summarizing. By sticking to a clean structure, you stop these frustrating roadblocks before they even start.
The core idea is simple: one row for each record, one column for each field, and one cell for each piece of data. This format is the universal language that Excel's most powerful analytical functions understand.
The infographic below shows how validating entries as you input them is a critical step in keeping this structure clean from the very beginning.
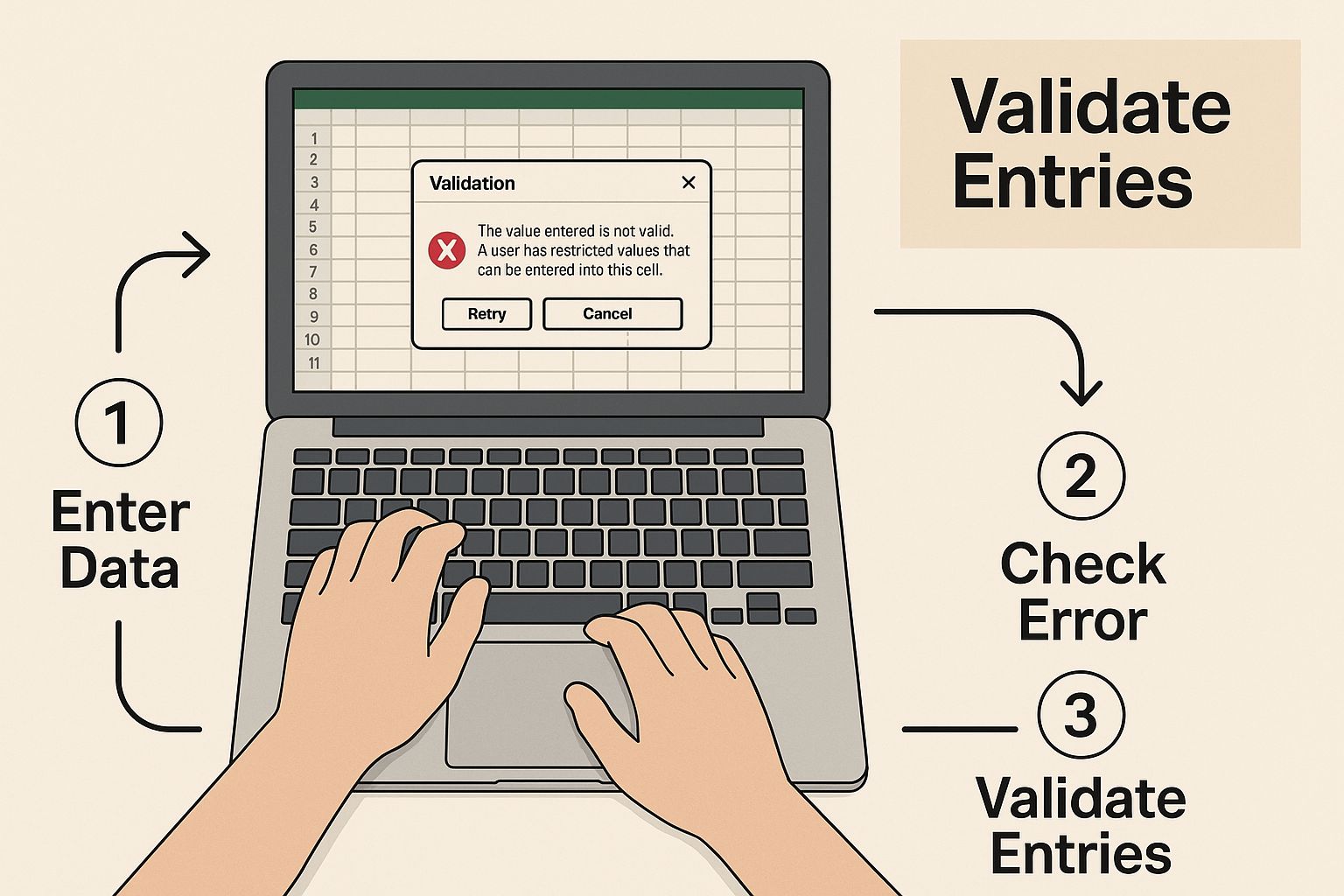
As you can see, proactive data validation acts like a gatekeeper. It ensures that the information entering your table already follows the rules you've set.
Spending a few minutes setting up your data correctly from the start will save you countless hours of cleanup and troubleshooting headaches down the road. A solid foundation isn't just a best practice; it's the absolute first step toward doing meaningful, reliable analysis in Excel.
Real-World Techniques for Cleaning Messy Data

Even if you've perfectly structured your spreadsheet, the data inside can still be a mess. We've all been there—typos, sneaky extra spaces, and inconsistent formats are the sworn enemies of good analysis. This is where the real work begins, turning you into a data detective hunting for the tiny flaws that can throw off your entire report.
Think of it like restoring a classic car. You have the solid frame (your data structure), but now it's time to polish the chrome and fix the dings. The good news is, Excel comes loaded with powerful tools to make this "restoration" process surprisingly efficient.
Despite all the fancy cloud platforms out there, Excel remains a go-to tool for a reason. Its simplicity and familiarity make it the perfect starting point for data processing, especially in large organizations. It’s the practical gateway to better data governance and smarter decisions, bridging everyday spreadsheet work with bigger enterprise goals.
Erase Hidden Errors with the TRIM Function
One of the most common—and infuriating—data problems is extra spaces. These invisible characters, often hiding at the beginning or end of your text, can stop your lookups and matches cold. A cell that looks like "John Smith" might actually be " John Smith ", which is why your VLOOKUP keeps failing.
The TRIM function is your best friend here. It zaps all leading and trailing spaces and shrinks any extra spaces between words down to a single one.
Here’s how it works:
- Messy Data: Imagine cell
A2contains" Jane Doe ". - Cleaning Formula: In a new column, you’d simply enter
=TRIM(A2). - Pristine Result: The formula gives you
"Jane Doe", a clean, reliable value ready for your analysis.
Standardize Entries with Find and Replace
Inconsistency is another major headache. One person enters "USA," another types "United States," and a third puts "U.S.A." If you want to group and analyze this data properly, you have to make them all the same. The Find and Replace tool (Ctrl+H) is perfect for this.
You can use it to methodically swap all variations for a single, standard term. This ensures that when you go to filter or build a PivotTable, everything lines up correctly. For a deeper dive into this and other powerful methods, check out our guide on how to clean data in Excel.
Split Jumbled Data with Text to Columns
Sometimes you inherit a spreadsheet where multiple bits of info are crammed into one cell. Think a full name like "John Doe" or a complete address like "123 Main St, Anytown, USA." To do any real analysis, you need to break that data apart into separate columns.
The Text to Columns feature was built for this exact scenario. It lets you split a cell's content based on a specific separator.
- Step 1: Highlight the column with the combined data.
- Step 2: Head to the "Data" tab and click "Text to Columns."
- Step 3: Choose "Delimited" and then select the character that separates your data (like a comma, space, or something else).
- Step 4: Excel gives you a quick preview. Once it looks right, click finish, and your data will be neatly split into new columns.
Automate Pattern Recognition with Flash Fill
Flash Fill is one of Excel's smartest tricks. It's like having a brilliant assistant who watches what you do, figures out the pattern, and does the rest of the work for you. It's a massive time-saver.
Flash Fill is a game-changer for extracting information. It's fantastic for pulling initials from names, separating area codes from phone numbers, or even building email addresses from first and last names.
See it in action:
Let's say you have a column of full names (e.g., "John Smith" in A2) and you want another column with just their initials.
- In cell
B2, you just type "JS" manually. - As soon as you move to cell
B3and start typing the next set of initials, Flash Fill jumps in, recognizing the pattern. - A grayed-out preview of the initials for the whole column pops up. Just hit Enter, and the entire column fills instantly. Magic.
Using Data Validation to Prevent Errors
The best way to fix errors is to stop them from happening in the first place. While cleaning up messy data is a crucial skill, a little proactive effort can save you from countless hours of headaches down the road. This is where Excel's Data Validation feature really shines, acting as a strict bouncer for every cell in your worksheet.
Think of it like setting the rules for a game before anyone starts playing. You get to define what's allowed and what isn't, turning your spreadsheet from a simple grid into a well-guarded fortress of reliable information. Instead of reacting to bad data, you prevent it from ever getting in.
Create Consistency with Dropdown Lists
One of the most common ways a dataset gets messy is through inconsistent text entries. Take a "Status" column, for example. One person might type "Complete," another "completed," and a third might just enter "Done." To a human, these all mean the same thing, but to Excel, they are four distinct values that will completely throw off your pivot tables and formulas.
Data Validation solves this beautifully by letting you create a dropdown list of pre-approved options.
- Enforce Uniformity: By limiting a cell's input to a specific list, you eliminate typos and variations.
- Improve User Experience: It's much faster and easier for people to just pick from a list instead of typing everything out.
- Reduce Cleanup: This simple step completely removes the need to standardize these entries later on.
Setting one up is straightforward. Just select the cells you want to control, go to the Data Validation menu, choose "List" from the "Allow" dropdown, and type your options into the "Source" box, separated by commas (e.g., In Progress,Complete,On Hold).
Set Boundaries with Number and Date Rules
Data Validation isn't just for text. It's incredibly useful for controlling numbers and dates, stopping illogical or impossible values from ever corrupting your data.
For instance, you can set a rule that an "Items Sold" column must only contain whole numbers greater than zero. If someone accidentally types -5 or 10.5, Excel will immediately reject the entry and pop up an error message. The same principle applies to dates. You can easily restrict entries to a certain timeframe, ensuring an order date can't be set for a day that hasn't even happened yet.
Data Validation transforms cells from passive containers into active guards. Each rule you set is a small but critical step toward building a dataset you can trust implicitly, protecting your analysis from the ground up.
The Data Validation dialog box is your command center for all of this, as you can see below.
This window is where you define criteria for all sorts of data types, from whole numbers and dates to text length and even custom formulas.
Implement Custom Validation Formulas
When you need to enforce more complex rules, Excel's custom formulas have your back. This opens up a whole new level of data quality control. One of the most powerful applications is preventing duplicate entries in a column that must be unique, like an "Invoice Number" or "Employee ID."
By using a formula like =COUNTIF($A:$A, A2)=1, you're telling Excel to reject any entry in column A if that same value already exists anywhere else in that column. It's a fantastic technique for maintaining the integrity of unique identifiers in your dataset. If you're looking for more ideas, we've put together a collection of Excel data validation examples with other practical uses.
A few minutes spent setting up these validation rules is an investment that pays for itself over and over. It strengthens your data, minimizes human error, and ensures the information you rely on for critical decisions is as accurate as possible.
How to Analyze Data and Find Hidden Insights
Alright, you’ve put in the hard work. Your data is clean, organized, and validated. Now for the fun part: making that data tell its story. This is where good data management in Excel truly pays off, transforming those neat rows and columns into actionable intelligence that can actually steer your business.
Excel is more than just a giant calculator; it’s loaded with features designed to help you dig deep, spot trends, and unearth insights that aren't just lying on the surface. The goal shifts from simply holding data to actively interrogating it. It’s all about using the right tools to slice, dice, and visualize your information to see what secrets it holds.
Let’s dive into the core tools that will help you do just that.
Unleash the Power of PivotTables
If there’s one killer feature for data analysis in Excel, it has to be the PivotTable. Think of it as a dynamic summary tool that lets you look at your data from any angle you want, all without writing a single formula. With a few simple drags and drops, you can take a massive, intimidating table and instantly boil it down to its essential points.
Instead of wrestling with complex formulas to figure out total sales by region or count products by category, a PivotTable handles it for you in seconds. It allows you to "pivot" your view—swapping rows and columns on the fly—to explore different relationships without touching your original data. It’s the ultimate sandbox for exploratory analysis.
A PivotTable can instantly answer questions like:
- Which product category brought in the most revenue last quarter?
- What were our top-performing sales regions each month?
- How many units did each salesperson move?
This ability to rapidly group and summarize information is what turns a messy dataset into a clear, concise report.
Answering Questions with Key Functions
While PivotTables are brilliant for big-picture summaries, sometimes you need to get granular and answer very specific questions right inside your dataset. That’s where Excel’s analytical functions really shine.
The magic of Excel functions isn't just about adding things up; it's about performing conditional calculations. You can stop summing an entire column and start summing only the rows that meet your exact criteria, giving you much more targeted and useful metrics.
Here are a few workhorse functions you'll use constantly:
- COUNTIF/COUNTIFS: Need to count cells that meet certain rules? Use these. For example, you can instantly find out how many projects are marked "Complete" or how many sales deals from the "North" region were over $1,000.
- SUMIF/SUMIFS: These work just like the counting functions but for adding values. They're perfect for calculating the total revenue from a specific product line or tallying up all expenses logged by a single department.
- XLOOKUP: This is the modern, super-flexible way to pull data from one table into another. It lets you find a value (like a
Product ID) in your sales table and grab corresponding information (likeProduct NameorPrice) from a separate product list. It’s a more intuitive and powerful replacement for older functions like VLOOKUP and is a real game-changer for enriching your data.
Make Data Pop with Conditional Formatting
Let's face it: our brains are wired to spot visual patterns much faster than we can read numbers in a grid. Conditional Formatting plays right into that strength by automatically changing how a cell looks—its color, font, or style—based on what's inside it.
This simple tool can make your data instantly more intuitive and easier to understand. You could use it to:
- Highlight all sales figures that beat your target in green.
- Create a color scale to build a "heat map" of your best-performing months.
- Flag any inventory levels that have dropped below a critical point in red.
By making important data points and outliers visually jump off the page, Conditional Formatting helps everyone see what matters at a single glance. For a full walkthrough of these techniques and more, you can explore our detailed post on how to analyze data in Excel. This guide offers step-by-step instructions for turning raw numbers into compelling intelligence.
Looking Ahead: Where AI and Excel Meet
For years, mastering Excel meant getting really good at structuring, cleaning, and analyzing data. Those fundamentals aren't going away, but a new layer is being added. Artificial intelligence is now working its way into spreadsheets, acting as a smart assistant that can handle the heavy lifting and find insights that used to take hours of painstaking work. This isn't just a gimmick; it's the next logical step for Excel.
AI is changing how we interact with our data. Instead of just telling Excel what to do with a formula, you can now collaborate with it. Imagine typing a simple question in plain English, like, "Show me a breakdown of last quarter's revenue by product category," and instantly getting a perfect PivotTable. This conversational style makes complex data analysis much more approachable.
Your New Data Assistant
With powerful AI add-ins like Elyx.AI, modern Excel can tackle jobs once reserved for data scientists. These tools are smart enough to figure out what you're trying to do, understand the context of your data, and run complex operations without you ever having to touch a tricky formula.
This shift is happening for a reason. The whole world of enterprise data management (EDM)—where Excel is a major player—is booming. It was valued at around USD 111.44 billion in a single year and is expected to grow at a rate of 12.11% annually. That puts it on track to be worth over USD 350 billion in less than a decade. You can dig into the numbers yourself in this enterprise data management market research report. This explosive growth comes from a massive demand for better, faster analytics, and that's exactly what AI in Excel delivers.
AI is already taking over some of the most frustrating parts of managing data:
- Automated Data Cleaning: AI tools can scan your entire dataset to find and flag inconsistencies, typos, and weird formatting, often suggesting the right fix.
- Formula Generation: Instead of wrestling with
VLOOKUPor nestedIFstatements, you can just describe the outcome you want, and the AI will write the formula for you. - Sentiment Analysis: Need to know how customers feel? An AI can actually read through a column of text feedback and tag each comment as positive, negative, or neutral.
It's like having an experienced analyst sitting over your shoulder. You can ask it to translate data, build a chart, or figure out why a formula is broken, all just by typing a simple request.
How You Can Use AI in Your Daily Work
Beyond creating quick summaries, AI is becoming a go-to tool for everyday tasks. You could use it to instantly translate a column of text from one language to another, which is a huge help for teams working across different countries. Or, when you’re completely stuck on a formula that keeps spitting out a #N/A error, you can just ask the AI chat why it's failing and get a clear, step-by-step answer.
The best part is that this is all happening right inside the Excel environment you already know. You don't have to migrate to a new platform to get these advanced capabilities. Your trusty spreadsheet is just getting smarter and more intuitive, solidifying its role as a must-have tool for anyone working with data today.
Common Questions (and Expert Answers) About Excel Data Management
Even when you follow all the best practices, you're bound to run into some specific roadblocks. It just happens. Let's tackle some of the most common questions I hear from professionals trying to get a handle on their data in Excel.
How Do I Handle Very Large Datasets Without Crashing Excel?
This is a classic problem. You have a massive file, Excel freezes, and your productivity grinds to a halt. The secret isn't a more powerful computer; it's using the right tools inside Excel.
Your best friend here is Power Query, which you'll find under the "Get & Transform Data" tab. Instead of dumping a giant dataset directly onto your worksheet (which is what causes most crashes), Power Query processes it in the background. It only shows you a preview, letting you work with millions of rows without overwhelming your system.
Here's another pro tip: save your file as an Excel Binary Workbook (.xlsb). It's a more efficient format that reads and writes data faster, often leading to smaller files and a much snappier feel. Also, be mindful of volatile functions like TODAY() or OFFSET(). Spreading them across thousands of cells forces Excel to recalculate constantly, which is a major drain on resources.
What Is the Best Way to Combine Data from Multiple Files?
Stop right now if you're manually copying and pasting from different workbooks. That's a surefire way to introduce errors and waste hours of your life.
Once again, Power Query is the hero. You can simply point it to a folder full of your Excel files, and it will consolidate everything into one clean, unified table for you.
The magic of this method is that the connection is live. When you drop next month's sales report into that folder, you don't repeat the process. You just hit the "Refresh" button in Excel, and the new data is instantly pulled in and added to your master table. It’s a game-changer for recurring reports.
Can I Really Trust Excel for Important Business Data?
Absolutely, if you use it the right way. For an enormous amount of business analysis and reporting, a well-structured Excel workflow is more than just reliable—it's incredibly powerful. The trust comes from applying the principles we've covered.
Think of it like building a house. You wouldn't trust a house built on a shaky foundation, right? It's the same with Excel. You build trust by:
- Enforcing data integrity with Data Validation to prevent bad data from ever getting in.
- Protecting your core worksheets to stop accidental edits to your raw data or crucial formulas.
- Keeping regular backups of any file you can't afford to lose.
Of course, if you're talking about enterprise-level needs—multiple people editing the same data at once, complex security rules, or millions of daily transactions—then a dedicated database is the right tool for the job. But for the vast majority of day-to-day analysis, planning, and reporting, a well-managed spreadsheet is a trusty and capable workhorse.
Ready to stop wrestling with the tedious parts of data management and just get to the insights? Elyx.AI plugs directly into your spreadsheet, letting you clean data, write formulas, and build summaries using simple, natural language. Let AI handle the heavy lifting so you can focus on what matters. Give it a try and see just how much time you get back in your day. Learn more and get started with Elyx.AI.
Reading Excel tutorials to save time?
What if an AI did the work for you?
Describe what you need, Elyx executes it in Excel.
Try 7 days free